When it comes to achieving optimal health and well-being, few factors are as vital as the strength and durability of our immune system. The immune system is a complex network of specialised cells that act as the body’s shield against harmful microbes, such as viruses, bacteria, and other intruders. An effective immune system shields us from infections and plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and longevity. What are some practical methods for enhancing our immune system?
In a world filled with constant threats to our immune system, such as evolving viruses and the stresses of modern life, it is crucial to prioritise and strengthen our immune support. Whether you’re a health enthusiast looking to optimise your immune function or searching for practical strategies to support immune health, there are numerous effective ways to boost your immune system for long-term well-being.
Immune System Boosting Foods
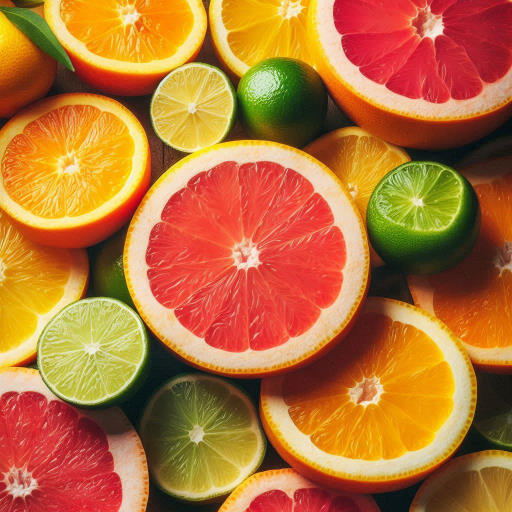 Citrus Fruits
Citrus Fruits
Citrus fruits like oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes are widely recognised for their impressive vitamin C content. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that is vital in supporting the production of white blood cells, which are essential immune system defenders. Antioxidants are crucial in neutralising harmful free radicals that can damage cells and contribute to various health problems. In addition to their immune-boosting potential, these fruits also contain flavonoids, which are compounds known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Adding citrus fruits to your diet is a delicious and refreshing way to give your body a healthy dose of essential vitamins, which can help strengthen your immune system.
Berries
Berries, including strawberries, blueberries, blackberries, and raspberries, are valuable sources of anthocyanins and quercetin. Anthocyanins and quercetin are crucial in fighting oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, and bolstering immune function. Berries contain anthocyanins that enhance the immune system by promoting the proper functioning of cytokines, which regulate the body’s inflammatory response. Incorporating berries into your diet can improve the development and proliferation of beneficial bacteria in your gut. The beneficial bacteria can remarkably strengthen the function of natural killer and phagocytic immune cells and enhance the activity of other immune cells like T cells. The diverse vitamins and minerals in vibrant fruits enhance the nutrient composition, thereby fortifying the immune system. These fruits contain many phytochemicals that offer numerous benefits for boosting the immune system. Not only are they delicious, but they also pack a powerful punch for strengthening immunity.
Leafy Green Vegetables
Spinach, kale and Swiss chard are incredibly nutritious and packed with vitamins, minerals and antioxidants that can do wonders for your health. Among these, vitamin A, vitamin C, and various forms of folate are crucial for bolstering immune function. Leafy greens are an excellent source of fibre, which plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. The gut’s beneficial bacteria thrive on the insoluble fibre found in these fibrous vegetables, allowing them to flourish and reproduce. Leafy green vegetables are essential to fortifying the immune system against harmful microbes, thanks to their rich blend of vital nutrients and powerful phytochemicals.
Onions
Onions have gained immense popularity as a widely cultivated and highly consumed vegetable worldwide. Their composition is impressive, consisting of a remarkable thirty-four phenolics, including a notable seventeen flavonoids. Among them, quercetin stands out as the most abundant. The compounds found in these substances possess remarkable antioxidant and anti-neuroinflammatory properties. Notably, the flavonoids present in onion peels exhibit substantial beneficial effects.
Quercetin is renowned for its anti-allergic properties, as it effectively regulates the immune system and prevents the release of histamines, which are responsible for triggering allergic reactions. Due to its beneficial properties, quercetin is commonly included in bronchial asthma and hay fever treatments. In addition to onions, quercetin can be found in various other foods, such as broccoli, apples, berries, grapes, certain herbs, tea, and wine. Garlic and onions are not only delicious additions to savoury dishes but also offer a flavorful way to enhance immune health.
Yoghurt and Probiotics
Yoghurt, along with other probiotic-rich foods like kefir and fermented vegetables, provides a source of beneficial bacteria that support a healthy gut microbiome. An optimal gut microbiome supports immune function by effectively regulating the body’s immune responses. Probiotics can boost the immune system by increasing antibody production and supporting the activity of immune cells. This helps the body defend itself against harmful microbes. Adding yoghurt and probiotic-rich foods to your diet can significantly impact your digestive health and immune system. Incorporating these foods into your diet can dramatically lower your chances of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Nuts
Almonds are known for their high vitamin E content, which can help support a healthy immune system. Research has demonstrated that when consumed with their skin, almonds can effectively inhibit the replication and transmission of viruses, including the herpes virus. The presence of specialised immune cells, including cytokines, interleukins, and tumour necrosis factors, is responsible for these effects.
Pistachios contain many beneficial compounds, including anthocyanins, flavonoids, and carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin, which are known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In addition to their delicious taste, these fruits are packed with essential vitamins that can help boost your immune system.
Walnuts are widely recognised for their exceptional health benefits. They possess a unique combination of natural compounds that synergistically contribute to reducing the risk of cancer. Resembling tiny brains, these little powerhouses are filled with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids known for their anti-inflammatory properties, essential for maintaining optimal brain health. In addition to their nutritional value, these fruits also boast a range of beneficial compounds, including tocopherols, antioxidant polyphenols, and ellagitannins.
When walnuts are consumed, ellagitannins transform into ellagic acid. Subsequently, the gut bacteria metabolise this compound, producing bioactive substances known as urolithins. Certain compounds, such as urolithin A, possess potent anti-inflammatory properties. Walnuts are rich in fibre, making them an excellent source of prebiotics for the beneficial bacteria in the gut. This can contribute to reducing the likelihood of developing diseases like colorectal cancer.
Similar to walnuts, pecans have a resemblance to miniature brains. They are rich in anti-inflammatory omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and immune-boosting vitamins E, folate, and zinc. These essential nutrients play a crucial role in supporting the body’s repair processes, bolstering the immune system to ward off infections, and safeguarding the integrity of our DNA. It is essential to understand that when DNA is damaged, it can lead to the development and proliferation of cancer cells. Incorporating pecans into your diet can lower cholesterol levels, decreasing the likelihood of developing heart disease.
In addition to almonds and walnuts, Brazil nuts are a valuable addition to support a healthy immune system. Brazil nuts are renowned as an exceptional dietary source of the highly beneficial antioxidant mineral selenium. This is essential for maintaining optimal thyroid gland function and safeguarding the integrity of our DNA. Brazil nuts can enhance the body’s natural antioxidant, glutathione, resulting in powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Brazil nuts have been shown to benefit individuals with chronic kidney disease significantly. The selenium content in these nuts helps to improve oxidative stress and reduce inflammation, making them a valuable addition to a kidney-friendly diet.
Seeds
Pumpkin seeds are packed with many essential nutrients that benefit your health. These include fibre, healthy fats, protein, vitamin E, zinc, magnesium, and folate. In addition, they contain various beneficial compounds, such as polyphenols, phytosterols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. These antioxidants are highly effective in combatting oxidative stress within the body. Research has discovered the significant benefits of these in enhancing the immune system. In addition to their nutrient profile, these products have effectively reduced the risk of infection by parasites, diabetes, high cholesterol, and even cancer.
Chia seeds are an excellent choice for boosting the immune system. These products contain a rich blend of both soluble and insoluble fibre. The insoluble fibre nourishes and supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, helping them thrive and outcompete harmful, infection-causing bacteria. The fibre also possesses a remarkable cleansing effect, effectively capturing and eliminating toxic chemicals contributing to high cholesterol and cancer, promoting a healthier body. Chia seeds contain various beneficial phytochemicals, such as quercetin, kaempferol, caffeic acid, and chlorogenic acid. These products combat inflammation and oxidative stress, providing essential support to the immune system. These products are specially formulated to promote heart and liver health and provide anti-cancer benefits.
Vitamins
Vitamin C
Furthermore, vitamin C is essential for preserving the resilience and vigour of the skin, in addition to the advantages previously highlighted. Ensuring the skin remains impenetrable to bugs and germs is crucial, as it is the body’s primary defence mechanism within the immune system. Vitamin C plays a vital role in the healing process of wounds and cuts. It helps protect against potential infections when bacteria enter the body through these openings.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an incredibly potent antioxidant that helps the body combat the harmful effects of oxidative stress. It also vitally bolsters the immune system by regulating cell signalling and gene expression. Vitamin E safeguards vascular health by preventing the adhesion of blood components to the walls of blood vessels, thereby promoting optimal blood vessel function. In addition, it enhances the production of prostacyclin, which aids in dilating blood vessels and inhibits the aggregation of blood cells.
Immune System Boosting Herbs and Spices
Garlic
Allicin, a compound found in garlic, is renowned for its potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties enhance the immune response, helping the body fight off infections. Garlic has long been celebrated for its numerous health benefits that have stood the test of time. Unfortunately, allicin, the active component found in garlic, gets destroyed when cooked.
New research indicates that garlic has the potential to enhance the immune system’s performance by activating various types of cells, including macrophages, lymphocytes, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, and eosinophils. It achieves this through multiple mechanisms, such as modulating cytokine secretion, stimulating immunoglobulin production, boosting phagocytosis (engulfing and digesting pathogens), and activating macrophages (cells responsible for engulfing and digesting cellular debris and pathogens).
Garlic’s therapeutic effects may be attributed to its impact on cytokine secretion, closely linked to the development and progression of various diseases associated with immune dysfunction. Garlic has been found to positively impact different health conditions, including obesity, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disorders, gastric ulcers, and cancer. Garlic appears to have a beneficial effect on the immune system, potentially enhancing its health benefits.
Ginger is known for its impressive anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, making it a valuable tool for ageing. The antimicrobial action of this product provides an additional advantage by aiding in the treatment of infections. Oxidative stress in the body arises when the production of free radicals or reactive oxygen species exceeds the antioxidant capacity. Imbalances of this nature have been associated with a range of health concerns, including heart diseases, neurodegenerative conditions, cancer, and the ageing process. The bioactive molecules found in ginger, particularly gingerols, have been shown to possess antioxidant properties in various situations. This suggests that they may be able to help mitigate the damaging effects of oxidative stress.
Turmeric
Turmeric, a remarkable spice derived from the roots of the Curcuma longa plant, offers numerous benefits for bolstering the immune system. Turmeric is packed with around fifteen polyphenols, with curcumin being the most potent and advantageous. Research has shown that curcumin has impressive anti-inflammatory properties and strong antioxidant effects.
Studies have indicated that curcumin can potentially impact the function of different immune cells, such as T cells, B cells, macrophages, and natural killer (NK) cells. These cells have vital functions in detecting and eliminating harmful bacteria and viruses. Turmeric, due to its antimicrobial properties, can enhance the immune system. It can effectively combat bacteria and fungi, thereby playing a crucial role in the prevention of infections.
Turmeric possesses powerful antiviral properties, effectively impeding the replication and dissemination of viruses. This treatment is highly effective against both the flu and human papillomaviruses. If left untreated, the latter can potentially develop into cervical cancer. Additionally, curcumin has been discovered to possess anti-cancer properties.
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a widely sought-after spice derived from the bark of trees belonging to the Cinnamomum family. Not only is it renowned for its delightful and comforting taste, but it also has the potential to boost the immune system. However, further research is necessary to gain a comprehensive understanding of the effects of cinnamon on the immune system. Cinnamon has various beneficial compounds that can do wonders for your health. These include cinnamaldehyde, cinnamic acid, proanthocyanidins, tannins, linalool, pinene, and eugenol. Cinnamon possesses remarkable properties, including its ability to combat bacteria, neutralise harmful oxidants, reduce inflammation, and fight against fungi. Cinnamon has demonstrated its potential as an anti-diabetic agent by aiding in diabetes prevention. Its ability to enhance insulin sensitivity contributes to regulating blood sugar levels. Cinnamon can lower the risk of viral infections by preventing viral cells from attaching to the body’s cells.
Basil
Basil, a wonderfully aromatic herb from the mint family, provides numerous advantages for bolstering the immune system. It is packed with a variety of beneficial compounds, including D-linalool, eugenol, catechins, quercetin, kaempferol, limonene, anthocyanins, terpinene, tannins, menthol, and rosmarinic acids, as well as powerful essential oils (23).
Basil possesses remarkable antibacterial and antiviral properties, thanks to the presence of linalool and eugenol. These potent compounds bolster the immune system, effectively defending against infections. Basil also possesses adaptogenic properties. Adaptogens are potent substances that aid the body in handling stress and promote a more robust immune system by enhancing the body’s ability to manage stress effectively (25).
Basil has been extensively studied and proven to be effective in treating cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders like diabetes and metabolic syndrome. In addition to its ability to safeguard the brain and liver, it also fortifies the immune system. These effects are attributed to its ability to reduce inflammation, combat oxidative stress, and fight against harmful microorganisms.
Rosemary
Rosemary enhances the taste of dishes with its aromatic flavour and provides potential benefits for supporting the immune system. Like other herbs, rosemary possesses many advantageous compounds that contribute to its remarkable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which in turn bolster the immune system. This impressive list of compounds consists of linalool, cineole, camphor, rosmarinic acid, limonene, and romano.
Rosemary possesses potent antioxidant properties. This is because it can activate superoxide dismutase, a natural antioxidant that our bodies produce. In addition to their culinary uses, thyme and sage also offer this particular benefit. Carnosic acid is present in the product, providing valuable antiviral properties. By inhibiting the replication of viral cells, this mechanism effectively prevents their multiplication. This product is highly effective in combating respiratory viruses.
Lifestyle Practices for a Robust Immune System
Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise provides a multitude of advantages that have a positive effect on the immune system. First and foremost, it enhances the efficiency of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system relies on consistent movement to ensure the circulation of lymph, as it lacks a pump similar to the heart’s function of pumping blood throughout the body.
Engaging in physical activity has been found to positively impact the production of immune cells, mainly white blood cells. These cells are essential for the body’s ability to fight off infections and protect overall health. Intense exercise for a brief duration can also boost the presence of natural killer cells in the body. On the other hand, engaging in rigorous activity for an extended duration does not provide any additional enhancement. After a prolonged, intense exercise, the levels of natural killer cells decrease. To enhance this aspect of immune health, it’s important to remember that less is more.
Considering the circumstances, engaging in physical exercise is ill-advised, mainly if you are dealing with an infection caused by a virus. This is due to the demonstrated ability to enhance viral replication and inflammation, particularly in viruses that impact the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Research has shown that maintaining a regular exercise routine can positively impact the immune system, decreasing infection symptoms and a shorter duration of illness. Regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of complications and mortality associated with life-threatening viruses like COVID-19.
Sleep
We know that insufficient sleep can lead to irritability, moodiness, and an unpleasant demeanour. We may sometimes experience a state commonly known as “hangry.” This state arises from the powerful fusion of hunger and anger, resulting in a potentially volatile emotional mix. When we don’t get enough sleep, our bodies produce more of the hunger hormone ghrelin. As a result, we tend to make less-than-ideal food choices when tired. These encompass a variety of processed foods that are rich in sugar, salt, and fat.
Weight gain can negatively impact the immune system. In addition, consuming a diet that is rich in sugar can lead to inflammation, weaken the immune system within hours, and heighten the likelihood of developing allergies.
Sleep plays a crucial role in safeguarding against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. During sleep, the glymphatic system efficiently eliminates plaques, waste, and proteins that play a vital role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Insufficient sleep can disrupt this process and disturb the blood-brain barrier, leading to potential long-term consequences such as an elevated risk of strokes, diabetes, and multiple sclerosis.
In addition, sleep also plays a crucial role in regulating learning and memory. One of the ways it achieves this is by exerting an influence on a substance known as brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Consistently depriving yourself of sufficient sleep can lead to a decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels. On the other hand, the perfect blend of temporary sleep deprivation and physical activity can enhance brain-derived neurotrophic factors in the hippocampus, a crucial brain region associated with memory. So, if you’ve had a rough night, it’s worth incorporating some exercise into your day. Not only will it help exhaust you, but it can also improve your chances of getting a good night’s sleep.
Ensuring a consistent and restful night’s sleep is crucial for maintaining a robust immune system. Adhering to proper sleep hygiene practices is also vital. This includes sleeping in a calm and dark room, keeping a consistent sleep schedule, refraining from screen time a few hours before bed to avoid blue light exposure, and seeking natural daylight. Click here to discover valuable insights on improving your sleep quality and conquering insomnia.
Stress reduction boosts the immune system.
When experiencing stress, the sympathetic nervous system triggers the release of substances that impact the immune system. These substances interact with receptors on white blood cells, affecting their functioning. Various immune cells, such as natural killer cells, B cells, and T cells, possess distinct receptors that can influence their response to stress.
Stress can significantly impact the immune system, affecting it through three interconnected systems within the body. The three axes involved are the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, the sympathetic–adrenal–medullary axis, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. These systems release hormones, including epinephrine, norepinephrine (adrenaline and noradrenaline), cortisol, prolactin, growth hormone, melatonin, β-endorphin, and enkephalin. Hormones attach to specific receptors on white blood cells, affecting their functionality. In times of stress, people often turn to alcohol as a coping mechanism, which can hurt their sleep patterns and ultimately weaken their immune systems.
When stress takes hold, it can disrupt the delicate balance of our immune system, leading to a host of interconnected health problems. Consider this perspective: stress can cause the system to respond as if constantly facing a persistent issue, similar to how it behaves in chronic inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. This modified immune function not only impacts our physical well-being but can also exacerbate psychological problems. For instance, in cases such as irritable bowel syndrome, stress can aggravate stomach issues due to the continuous release of cortisol.
Excessive stress can result in elevated levels of substances such as proinflammatory cytokines, which have been associated with conditions such as schizophrenia. Chronic stress has been found to potentially heighten the likelihood of developing autoimmune diseases. Scientists are investigating the intricate relationship between autoimmune diseases and their impact on our body’s stress response. By gaining a deeper understanding of this phenomenon, we can develop strategies to mitigate the immune reactions caused by stress, ultimately enhancing the well-being of individuals suffering from autoimmune conditions.
In conditions like multiple sclerosis, stress triggers specific substances in the brain that lead to inflammation, exacerbating the disease. Implementing effective stress management strategies is crucial for safeguarding the immune system. These techniques encompass controlled breathing, mindfulness practices, meditation, and therapeutic conversations.
Reducing Alcohol to Boost the Immune System
When someone consumes alcohol, their body focuses on expelling it as quickly as possible. This is because the body recognises alcohol as a toxin and prioritises its elimination above all else.
Consuming alcohol can have detrimental effects on the cells that form the lining of the digestive system, increasing the risk of microbes and toxins being able to penetrate the bloodstream. In addition, it can potentially harm the T cells and neutrophil immune cells. Alcohol can potentially disrupt the delicate balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which can negatively impact immunity in the gut. The effect on the gut microbiome and intestinal lining facilitates the infiltration of bacteria into the bloodstream, potentially inciting liver inflammation that may ultimately culminate in liver disease and cancer. Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with the development of lung and respiratory diseases.
Both long-term drinking and binge drinking can have adverse effects on immunity. Interestingly, even minimal alcohol consumption can have an impact on the immune system. Alcohol has a way of loosening inhibitions and encouraging people to step outside their comfort zones. This increases their vulnerability to accidents, including burns, severe bleeding, or even head injuries. Regrettably, the process of recovering and healing from these conditions may be hindered by the detrimental effects of alcohol on the immune system. It is highly advantageous to limit alcohol consumption and refrain from excessive drinking to safeguard the immune system.
Various factors can impact the immune system, including diet, exercise, sleep, stress, and alcohol consumption. This article provides valuable tips on safeguarding the immune system, allowing individuals to enjoy a long and healthy life. Nevertheless, it is crucial to remember that life is meant to be lived, adhering to the age-old adage of “everything in moderation.” But you can safeguard your immunity while still indulging in the pleasures of life.
References
Exercise and the immune system
Immune boosting benefits of vitamins and minerals
The Article: Effective Ways to Boost the Immune System Appeared First On Nutritionist Kempsey.
The Article: Proven Methods for Enhancing the Immune System appeared first on Jane Stevens.
The Article Proven Methods for Enhancing the Immune System Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com



Comments are closed