When planning electrical installations for your home or commercial space, a common question arises regarding the necessity of a main breaker in a sub panel. This inquiry often emerges as property owners contemplate upgrading their electrical systems or adding new circuits to accommodate growing power demands. Grasping the role and requirements of sub panels is crucial for establishing a safe, functional, and efficient electrical infrastructure that meets your needs.
In most scenarios, a sub panel does not mandate a main breaker since it derives power from the main panel, which is already equipped with a main breaker that controls the total power supply. The breaker in the main panel acts as the primary disconnect for the entire electrical system, including all sub panels. However, certain local electrical codes or specific installation stipulations may necessitate the inclusion of a main breaker in sub panels, particularly for enhanced safety or operational convenience. Always verify your local regulations to ensure compliance and safety.
Although not universally required, integrating a main breaker into your sub panel can yield multiple advantages. It provides a quick and straightforward way to disconnect power to all circuits within that panel without disrupting the entire electrical system. This feature is especially beneficial during maintenance or emergencies, as it facilitates the safe isolation of various sections of your property’s electrical network, ultimately enhancing safety and accessibility during such critical situations.
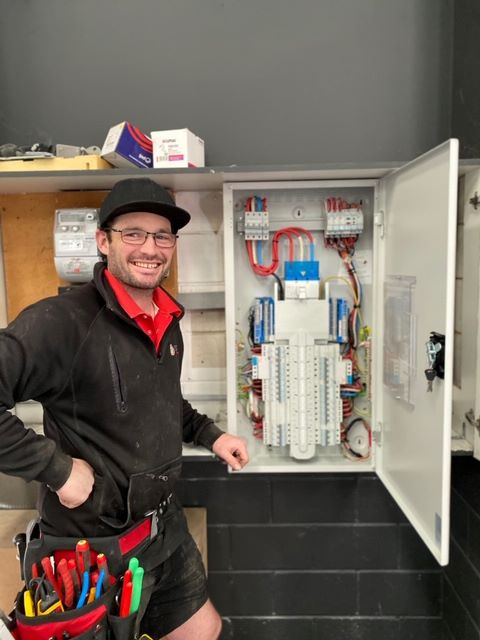
Explore the Key Functions and Advantages of Sub Panels for Electrical Systems
Sub panels serve a vital function in electrical systems by enabling effective power distribution to specific areas or appliances within a property. They significantly enhance the control and organization of circuits while improving the overall capacity to manage electrical loads. By strategically placing sub panels throughout your property, you can optimize your electrical infrastructure to efficiently meet the demands of various appliances and equipment, ensuring that your home or business runs smoothly.
Grasping the Importance of Sub Panels: Their Fundamental Role and Advantages
A sub panel, often referred to as a subsidiary panel or distribution board, functions as an additional electrical panel that branches off from the main electrical panel. Its primary purpose is to act as a secondary distribution point for electricity throughout a building, offering flexibility and enhanced efficiency. Sub panels are typically installed to:
- Enhance circuit capacity for a variety of applications and equipment.
- Isolate power supply to specific areas or devices for improved safety and convenience.
- Facilitate better organization and management of the entire electrical system.
Common locations for sub panels include garages, workshops, or larger homes where the main panel may be positioned far from areas that require power. By utilizing sub panels, property owners can achieve more efficient power distribution, simplifying circuit management and enhancing the accessibility and control of their electrical infrastructure.
Crucial Factors to Assess for Electrical Load Before Installing a Sub Panel
Before embarking on a sub panel installation, it is essential to thoroughly evaluate the electrical load requirements. Key factors to consider include:
- The total amperage needed for the designated area or equipment.
- The number and types of circuits necessary for specific applications.
- The distance from the main panel to the selected sub panel location.
Calculating the anticipated load is vital to ensure that the sub panel can safely accommodate it. Typically, sub panels come in capacities ranging from 60 to 200 amps, depending on their intended use. Matching the sub panel’s capacity to your specific electrical demands is crucial for both operational efficiency and safety. Additionally, considering potential future expansions when sizing your sub panel can save time and costs, preventing the need for upgrades or replacements as your electrical requirements evolve.
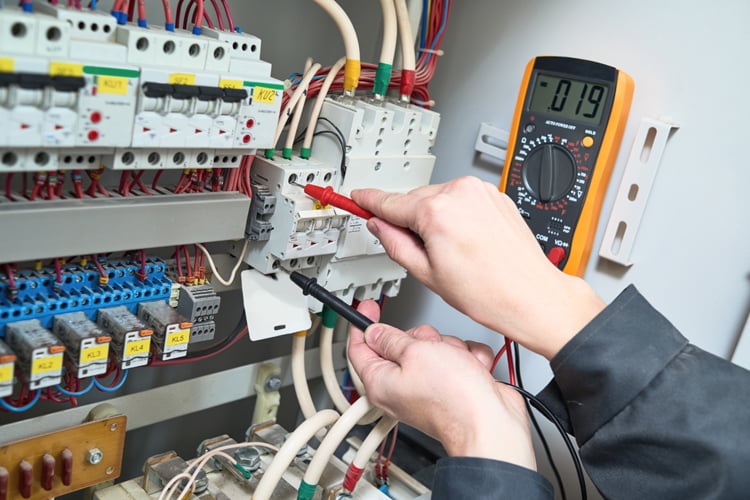

Essential Elements to Ensure Safe and Effective Sub Panel Installation
To guarantee a safe and efficient installation of a sub panel, several critical considerations must be addressed. These include circuit breakers, adherence to regulatory standards, and the implementation of necessary safety measures. Understanding these installation requirements is paramount for establishing a safe, reliable, and compliant electrical system that protects your property and its occupants.
Evaluating the Need for Circuit Breakers in Sub Panels
While sub panels do not always require a main breaker, the necessity may vary depending on specific circumstances, such as:
- The distance from the main panel: A local disconnect may become essential if the sub panel is located far from the main panel.
- The number of circuits: Sub panels with more than six breakers typically require a main breaker to enhance safety and compliance.
- Local codes: Some jurisdictions mandate the installation of main breakers in all sub panels.
A main lug sub panel relies on the main breaker from the main panel for overcurrent protection, a common setup when the sub panel is positioned close to the main electrical panel. Understanding the specific requirements of your installation is crucial for both compliance and safety, ensuring that your electrical system operates optimally.
Understanding Regulatory Standards for Sub Panel Installations
In Australia, specific electrical standards govern the installation of sub panels, which include:
- AS/NZS 3000: This standard outlines the comprehensive requirements for all electrical installations.
- Maximum rating: Main breakers for sub panels must not exceed the ampacity of the feeder conductors to ensure safe operation.
- Labelling: Clear identification of the power source for the sub panel is a mandatory requirement.
Adhering to these standards is essential for guaranteeing safety and legal operation. It is highly advisable to consult local authorities regarding specific regional requirements, and remember that all electrical work must be performed by a licensed electrician to ensure compliance and safety!
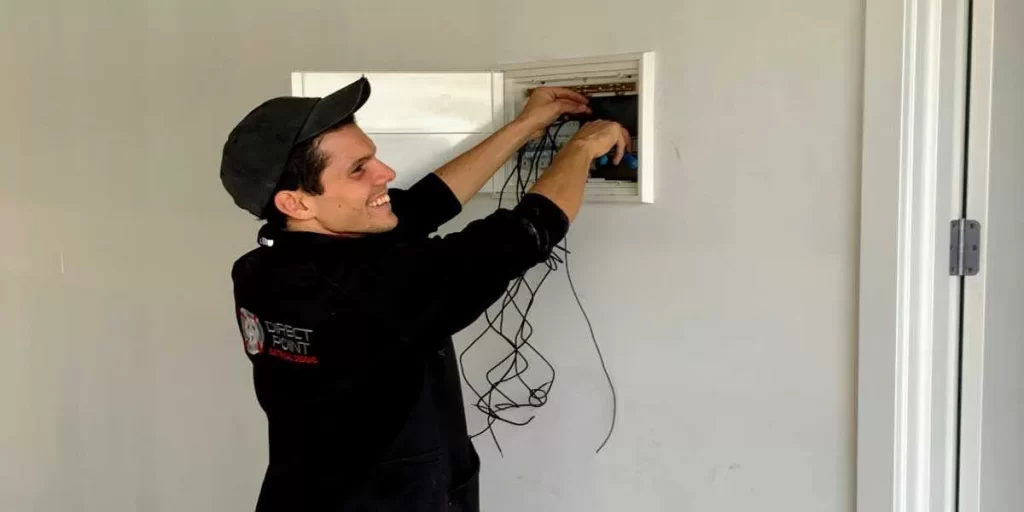

Implementing Essential Safety Measures for Sub Panel Installations
Implementing robust safety measures during sub panel installations is crucial to mitigate electrical risks and ensure operational safety. Important considerations include:
- Proper grounding: Ensure that the sub panel is effectively grounded to reduce the risk of electrical shocks and enhance safety.
- Adequate spacing: Maintain sufficient clearance around the panel to facilitate easy access and adequate ventilation, preventing overheating.
- Weatherproofing: For installations located outdoors, utilize weather-resistant enclosures to protect against moisture and other environmental factors.
Moreover, it’s vital to utilize the correct wire sizes and types tailored to the expected load. Installing arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in accordance with code requirements is also essential for ensuring safety. Regular inspections and maintenance of the electrical installation significantly contribute to ongoing safety and compliance. Always engage a licensed electrician for sub panel installations to ensure that all safety standards are rigorously adhered to, providing peace of mind for property owners.
Addressing Common Questions About Sub Panels and Main Breakers
The complexities surrounding sub panels, including considerations about breakers, sizing, and regulatory compliance, can be overwhelming for property owners. Gaining a clear understanding of the essential requirements is crucial for ensuring a safe and compliant electrical setup that meets all local codes and safety standards, ultimately protecting your investment.
Is it Necessary for a Sub Panel to Have a Main Breaker?
A sub panel does not necessarily require a main breaker. The necessity largely depends on its location in relation to the main panel and local electrical codes. If the sub panel is situated within the same building as the main panel, a main breaker is typically not a requirement.
However, if the sub panel is located in a separate structure, it generally must include a main breaker for safety and compliance reasons, ensuring that all electrical installations adhere to local regulations and standards.
Can a Main Breaker Panel Function as a Sub Panel?
Yes, a main breaker panel can indeed function as a sub panel, although it may not always be the most efficient choice. In this scenario, the main breaker would serve as an additional disconnect point rather than the primary disconnect for the electrical system.
Opting for a panel specifically designed as a sub panel is generally more cost-effective and space-efficient, providing better functionality for your electrical needs while enhancing overall system performance.
What Size Breaker is Suitable for a 100 Ampere Sub Panel?
For a 100 ampere sub panel, it is standard practice to use a 100 ampere breaker in the main panel to feed it. This breaker should match the sub panel’s rating to ensure optimal protection and functionality, providing a reliable and consistent power supply.
Additionally, the wire size must also be adequate for handling a 100 ampere load, ensuring that the entire electrical system operates safely and effectively without risking overheating or electrical failures.
What Regulations Govern Electrical Sub Panels?
Electrical sub panel regulations can vary by region, but they primarily focus on safety and accessibility. Key regulations typically include:
- Proper grounding and bonding procedures to enhance safety and prevent electrical hazards.
- Correct wire sizing to accommodate anticipated loads effectively and prevent overloads.
- Adequate spacing around the panel to ensure accessibility and safety for maintenance.
- Clear labelling of all circuits within the panel for better management and quick identification.
Always refer to local codes and consider professional installation to ensure full compliance with all regulations, creating a safe electrical environment for your property.
What is the Capacity Limit for a Sub Panel Connected to a 200 Ampere Main Panel?
A sub panel linked to a 200 ampere main panel does not have a fixed capacity limitation. The size of the sub panel is contingent on several factors, including:
- The available capacity in the main panel to support additional loads without risking overload.
- The intended load requirements for the sub panel based on its specific usage and applications.
- The wire size employed between the panels, ensuring it can safely handle the load without overheating.
It is entirely feasible to install a 100 or 150 ampere sub panel, provided that the main panel has sufficient spare capacity to support it, offering flexibility for future electrical needs as your requirements evolve.
How Does One Accurately Size a Breaker for a New Sub Panel Installation?
To effectively size a breaker for a new sub panel, follow these steps:
- Calculate the total load that the sub panel is expected to support, considering all connected devices and their amperage requirements.
- Select a panel that is rated for that load or higher to ensure safety and prevent overload.
- Choose a breaker in the main panel that aligns with the sub panel’s rating for optimal performance and protection.
It is wise to consider future expansion needs when sizing the panel. Often, installing a slightly larger panel than currently required can provide additional flexibility for accommodating future electrical demands, making your system more adaptable and efficient.
The Article: Does a Main Breaker Need to Be in a Sub Panel? first appeared on https://writebuff.com
The Article Main Breaker Requirements for Sub Panels Explained Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com





Comments are closed